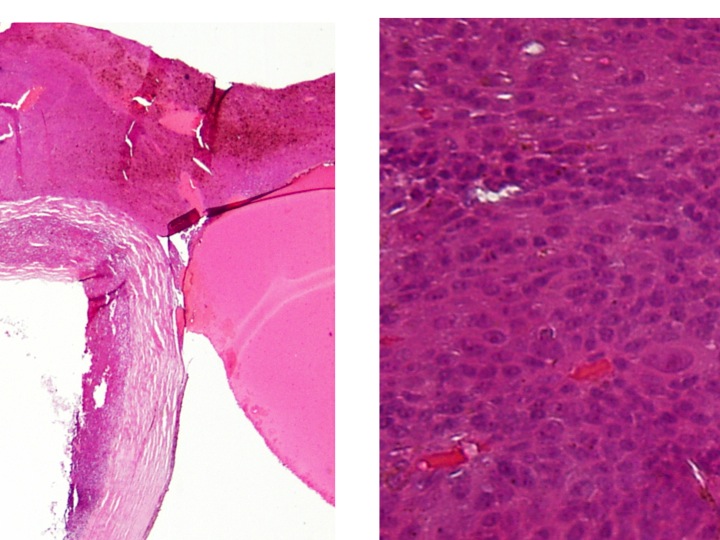
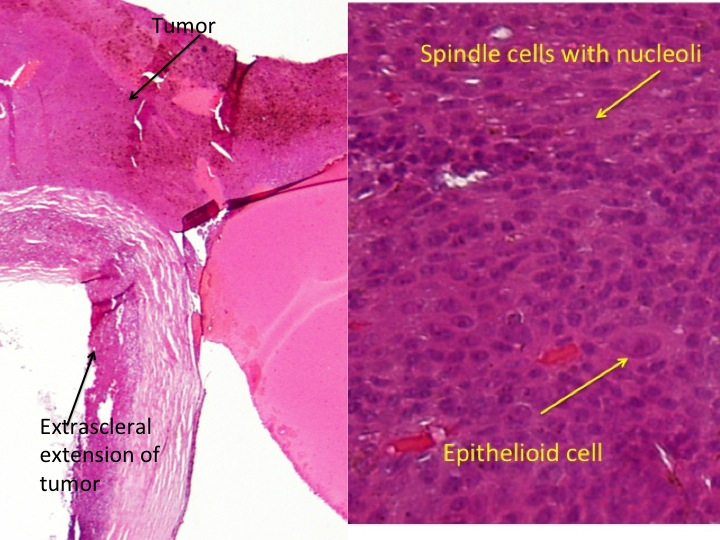
One should immediately recognize that the lesion is a melanoma arising from the uveal tract, particularly the choroid.
Choroidal melanomas are classified based on the shape of the melanoma cells (Callendar classification):
- Spindle A cells are spindle (or cigar-like) in shape, with a slender nucleus, fine chromatin, and an indistinct nucleolus.
- Spindle B cells have a shape similar to that of Spindle A cells, but the nucleus is more plump and the nucleolus is rather distinct.
Epithelioid cells are larger cells and exhibit more pleomorphism. They have a polyhedral shape as well as a richly-staining nucleolus. One should see the
presence of epithelioid and Spindle B cells in the higher magnification image. Thus, this is a
mixed cell melanoma per the Callendar classification system.
One of the most important features of the tumor seen in the histopathology photos is
extrascleral extension (which can be observed on the lower magnification image). It is important to know that the sclera provides a barrier to egress of uveal melanomas and that
invasion of the orbit occurs along the emissaries of the vortex veins and the ciliary arteries and nerves. If given sufficient time, however, choroidal melanomas can cause necrosis of the sclera and invade extraocular tissues through this weakness. Most uveal melanomas that extend into extraocular tissue are large tumors.